Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries, from healthcare to autonomous vehicles. But running AI algorithms efficiently requires specialized hardware — this is where AI accelerators come in. Whether you’re a student, a beginner in hardware design, or an experienced engineer, understanding AI accelerators is essential for modern digital design.
In this article, we’ll explain what an AI accelerator is, why it matters, and provide a block diagram along with the basic building blocks, and finally tips for designing efficient AI accelerator.
What Is an AI Accelerator?
An AI accelerator is a specialized hardware designed to speed up AI-related computations, such as neural network inference and training. Unlike general-purpose CPUs, AI accelerators such as NPUs are optimized for the mathematical operations common in AI workloads — mainly matrix multiplications and convolutions. AI accelerators focus on parallelism, data reuse, and specialized datapaths to achieve high throughput and low power consumption.
Why Use AI Accelerators?
- Performance: Accelerate AI computations by orders of magnitude.
- Energy Efficiency: Perform AI tasks with less power consumption.
- Real-time Processing: Enable AI applications on edge devices like smartphones and IoT gadgets.
- Offload CPUs: Free up general-purpose processors for other tasks.
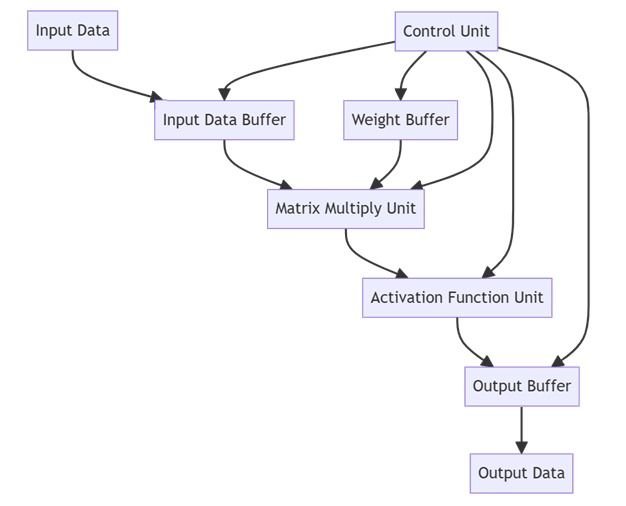
Basic Building Blocks
A typical AI accelerator includes:
- Matrix Multiply Unit: Core engine for AI computations; performs bulk matrix operations.
- Activation Function Unit: Applies nonlinear functions like ReLU, sigmoid, or tanh.
- Weight and Input Buffers: Store weights and input data close to compute units to reduce latency.
- Control Unit: Manages operation sequencing, data movement, and operation timing.
- Output Buffer: Holds intermediate and final results before transfer.
- Interconnects and Data Paths: Connects all units efficiently to maximize throughput.
Simple Block Diagram
Tips for Designing Efficient AI Accelerator
- Optimize data flow: Minimize data movement to save power and increase speed.
- Use parallelism: Exploit hardware parallelism for matrix and vector operations.
- Design modular blocks: Separate compute, memory, and control units clearly.
- Implement pipelining: Improve throughput by overlapping operations.
- Plan memory hierarchy: Use caches and buffers effectively for AI workloads.
AI accelerators are critical for efficient AI workloads, and understanding their hardware design is invaluable. Whether you’re learning or designing advanced hardware, mastering these fundamentals will empower you to tackle complex AI hardware challenges.
Want to learn, how to build your first AI accelerator hardware – Go through the article: Matrix Multiply Unit: Architecture, Pipelining, and Verification Techniques
Discover more from VLSIFacts
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.