Syntax: #delay
It delays execution for a specific amount of time, ‘delay’.
There are two types of delay assignments in Verilog:
Delayed assignment:
#Δt variable = expression; // “expression” gets evaluated after the time delay Δt and assigned to the “variable” immediately
Intra-assignment delay:
variable = #Δt expression; // “expression” gets evaluated at time 0 but gets assigned to the “variable” after the time delay Δt
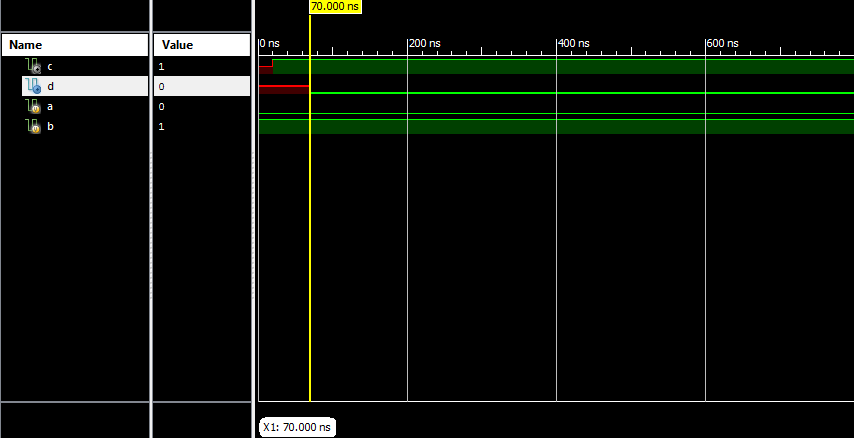
Example:
module delay_test(
input a, // Assume a=0 initialized at time 0
input b, // Assume b=1 initialized at time 0
output reg c,
output reg d);
initial
begin
#20 c = (a|b); //a|b gets evaluated after 20ns and gets assigned to ‘c’ immediately
d = #50 (a&b); //a&b gets evaluated at time 20ns but gets assigned to ‘c’ after 70ns (20ns+50ns)
end
endmodule
Note: #(delay) can not be synthesized. So we do not use #(delay) in RTL module to create delay. There are other methods which can be used to create delays in RLT module. #(delay) can be used in testbench files to create delays.
Discover more from VLSIFacts
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.